Exploring Multi-Directional Wheels: A Technological Insight

The wheel, a foundation of human innovation, has undergone significant evolution since its inception. This evolutionary trajectory takes us from simple circular objects to sophisticated multi-directional wheels.
Today, these advanced wheels are a pivotal innovation, redefining motion in numerous technological and industrial arenas. They empower machinery and devices with unprecedented maneuverability and efficiency.
Multi-directional wheels emerged as a revolutionary element in modern engineering, offering flexibility and precision in movement that traditional wheels cannot match.
The Mechanics of Multi-Directional Wheels

The fundamental characteristic of multi-directional wheels is their capacity to enable simultaneous motion along multiple axes. Unlike conventional wheels that roll strictly forward or backward, these wheels incorporate additional degrees of freedom.
They achieve this through a central hub that rotates in the primary direction, surrounded by peripheral rollers. These rollers are mounted at an angle, usually 45 degrees, to the wheel’s axis.
Design and Structure: Core to Functionality
The design of these wheels is a marvel of engineering precision. The central hub ensures standard motion, similar to traditional wheels. However, the distinctiveness arises from the peripheral rollers.
These rollers are free to rotate independently, allowing side-to-side movement in addition to the traditional rolling motion. The orientation and interaction of these rollers with the surface enable the wheel to move in any direction without the need for a pivot.
Rollers: The Pivotal Elements

Figure 2: Multi-directional wheel with 10 rollers.
Rollers are the critical components in multi-directional wheels. Their design, usually cylindrical with smooth or textured surfaces, significantly influences the wheel’s performance. The material of the rollers, often a durable polymer or rubber, ensures grip and durability.
The arrangement and angle of these rollers dictate the wheel’s responsiveness to multidirectional forces, offering a seamless transition between directional changes.
Related: Drive Wheels: Are They the Future?
Types of Multi-Directional Wheels:

Figure 3: Omni and Mecanum wheels.
A. Omni Wheels:
The Omni Wheel incorporates smaller rollers around its circumference, mounted in such a way that they can roll independently of the wheel itself. This configuration allows the wheel to move side to side and turn with ease without changing the direction it’s facing.
The design of the Omni wheel is focused on minimizing friction when changing directions, which is essential for applications like conveyor belts and turntables, as well as robotics, where multidirectional movement and quick, agile changes in direction are required.
Related: Omnidirectional Wheels Movement for Material Handling Applications.
B. Mecanum Wheels:
Mecanum wheels are characterized by their angled rollers attached around the circumference. Each roller is positioned at a 45-degree angle to the wheel’s plane, allowing for lateral movement when the wheels on one side rotate opposite to those on the other.
This design enables the wheel to move in any horizontal direction by varying the rotational direction and speed of each wheel. Applications of Mecanum wheels are vast, ranging from automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in manufacturing facilities to robotics in warehousing, where the ability to sidestep and maneuver in tight spaces is crucial.
In comparison, Mecanum wheels have larger rollers, angled diagonally, enabling more complex movement patterns. In contrast, Omni wheels have smaller, more numerous rollers that provide smoother multidirectional movement.
Maintenance and Longevity of Multi-Directional Wheels:
Multi-directional wheels, due to their design, distribute wear across multiple rollers. Regular inspection is crucial, as worn rollers can impede wheel performance and maneuverability. Rollers, being contact points, are prone to the most wear and should be checked routinely for signs of degradation.
To extend the life of multi-directional wheels, consistent maintenance is key. Regular cleaning to remove debris, lubrication of moving parts, and tightness checks of attachment points are essential. This routine care prevents premature wear and ensures optimal functionality.
While maintenance incurs a recurrent cost, it is generally more cost-effective than replacing multi-directional wheels. Timely maintenance can prevent the need for frequent replacements, thereby reducing long-term expenses. Strategic maintenance schedules aligned with usage intensity can optimize both performance and expenditure.
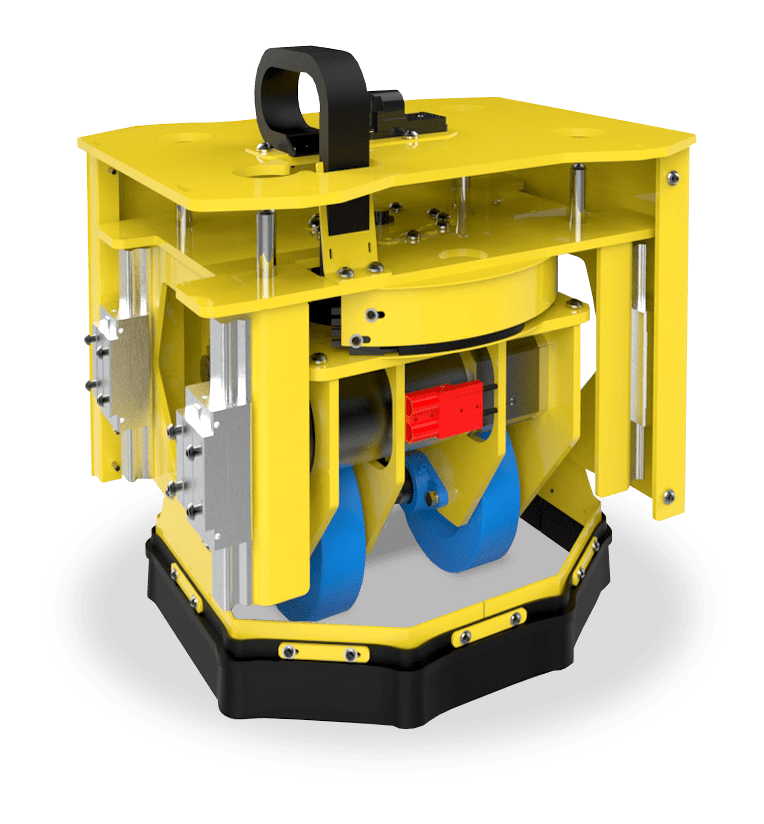
The Conceptual Advantage: HaloDrive by Conceptual Innovations

Figure 4: HaloDrive pod.
Halodrive systems emerge as an innovation in multi-directional wheel technology, setting a new standard for heavy-duty industrial movement. Its sophisticated design permits modular integration, making it a versatile solution for extreme-duty applications.
- Robustness Meets Sophistication:
Capable of handling up to 100 tons and accommodating dimensions up to 250 feet, it boasts precision positioning with an accuracy of plus or minus 0.5mm. This level of precision is unparalleled, especially considering the size and weight capacities involved. - Unmatched Efficiency and Adaptability:
HaloDrive’s design negates the need for facility alterations, special flooring, or ancillary infrastructure, such as rails or tracks. This adaptability allows for the retrofitting of existing equipment, providing a cost-efficient mobility upgrade that slashes overall equipment expenses. - Precision and Safety:
The Halodrive pods deliver exact positioning, enhancing operational productivity without necessitating specialized skills. They offer a significant safety margin by reducing the risk of injuries and damage, thereby fostering a safer workplace. The motorized mechanism eases the operator’s workload, allowing for the effortless maneuvering of substantial loads.
HaloDrive Pods in Action:
HaloDrive Pods excel in omnidirectional steering, allowing each pod to act independently for highly precise movements. They enable equipment to start motion in any direction, navigate through constrained spaces, and execute turns with minimal radius.
This agility is particularly beneficial for sectors that handle large-scale manufacturing and maintenance, like aerospace, automotive, maritime, and heavy machinery industries.
Related: Developing HaloDrive™ Platforms with Omnidirectional Maneuverability
Conceptual Innovations: Pioneering the Multi-directional Future
Conceptual Innovations stand at the forefront of industrial mobility, engineering solutions that drive material handling forward. Their commitment to innovation is evidenced in their diverse product range, such as HaloDrive™ pod, drive cart, and drive caster. These products enhance the functionality and range of motion for various applications.
For those looking to propel their operations into the future with Conceptual Innovations’ advanced systems, reaching out to their expert team can pave the way for optimized material handling solutions. Connect with a HaloDrive product engineer to explore tailored solutions for your specific needs.
